Modulation
Modulation allows a primary or advanced function to be adjusted in real-time by any of the other output channels or by any of the available input sources. Most parameters can be modulated.
There are two main modes of modulation, “Threshold based” and “Curve based”. Threshold means to apply a state change when the modulation source reaches a threshold value, e.g. Sample & Hold uses this technique. The other main mode is “Curve based”, where curves are used to calculate a new value, e.g. Amplitude uses this technique.
All modulations can be configured via the Parameter Screen for a given parameter.
Threshold modulation settings
| Setting | Function |
| Source | Sets the modulation source, this can be any of the internal or external channels |
| Threshold | Threshold limit to apply a state change |
Curve modulation settings
| Setting | Function |
| Source | Sets the modulation source, this can be any of the internal or external channels |
| Type | Linear or Exponential |
| Index | Wet/dry mix. A value of 100 has maximum effect, a value of 0 has no effect. A value of -100 will invert the CV (useful for 0-5V input signals) |
Linear & Exponential Curves
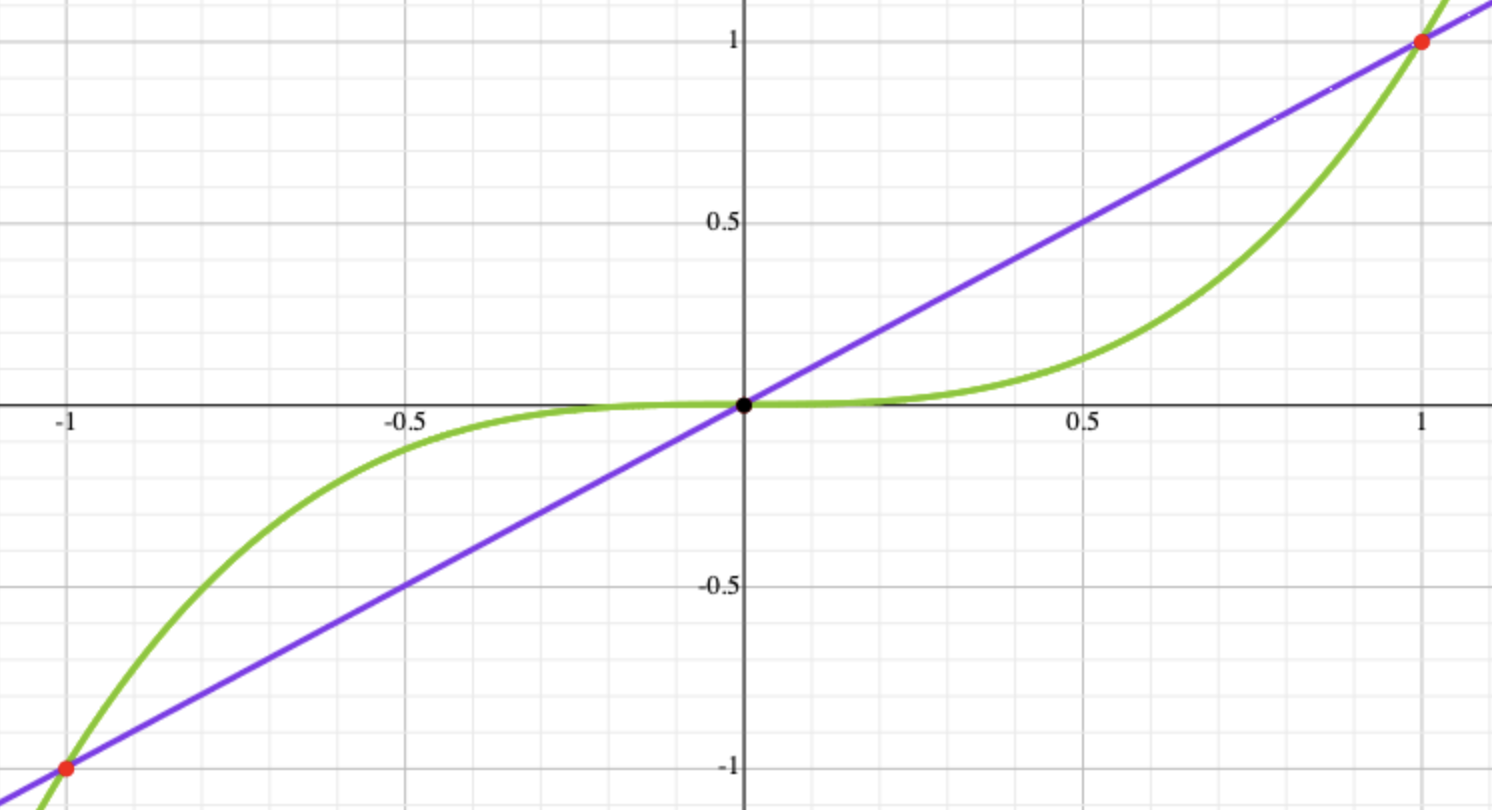
- Horizontal axis is the normalized modulation source amount
- Vertical axis the the normalized modulated result
- The origin point, (0,0) is the current value of whatever setting is being modulated. For example, if
Amplitudeis being modulated, and the amplitude value chosen is 30%, then the origin point describes a value of 30%. When the CV source for modulation is 0.0V, then the result will be 30%, when the CV source is greater than 0.0V or below 0.0V, then theAmplitudewill increase or decrease above or below 30% as described by the curve.
NOTE: Additional clamping curves apply to Frequency modulation in the sub 1Hz range. |